Pioneering Quantum Communication with Orbital Angular Momentum
The ADAMANT project, spearheaded by the Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN), is at the forefront of developing a comprehensive quantum communication system. This system integrates a quantum radiation source endowed with orbital angular momentum (OAM) and an innovative detection mechanism. The primary goal is to establish a robust framework for long-distance quantum communication, leveraging the unique properties of OAM to enhance information transfer.
Traditional quantum communication systems often rely on the polarization states of photons, which, while effective, are limited to two-dimensional encoding. In contrast, OAM offers access to a high-dimensional state space, enabling the encoding of more information per photon. This high-dimensional encoding not only increases the data capacity but also enhances the security of quantum communication protocols, as it becomes more challenging for eavesdroppers to intercept and decode the information without detection.
A significant advantage of utilizing OAM in quantum communication is its resilience to misalignments between the transmitter and receiver.Unlike polarization-based systems, which require precise alignment, OAM-based systems can maintain communication integrity even when the relative orientation of the communicating parties varies.This feature is particularly beneficial for free-space communication scenarios, such as satellite-to-ground links, where maintaining strict alignment is challenging.
The ADAMANT project also aims to demonstrate, for the first time, the feasibility of locally measuring quantum radiation with OAM. To achieve this, the project will develop a novel interferometric method capable of detecting OAM quantum states even at positions distant from the beam’s singularity. This advancement is crucial for practical implementations, as it allows for more flexible and scalable detection architectures in quantum communication networks.
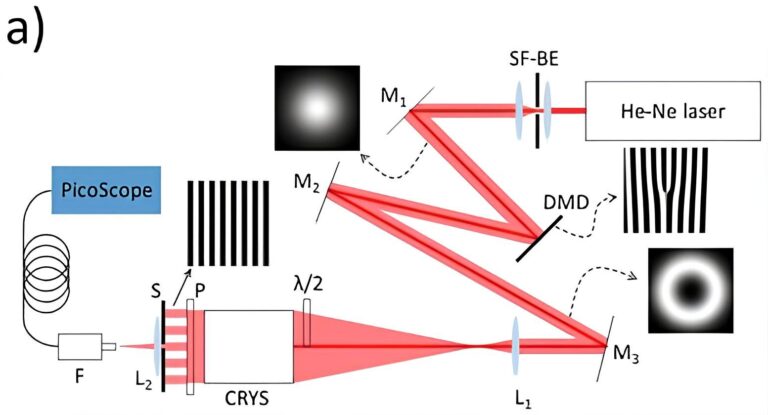
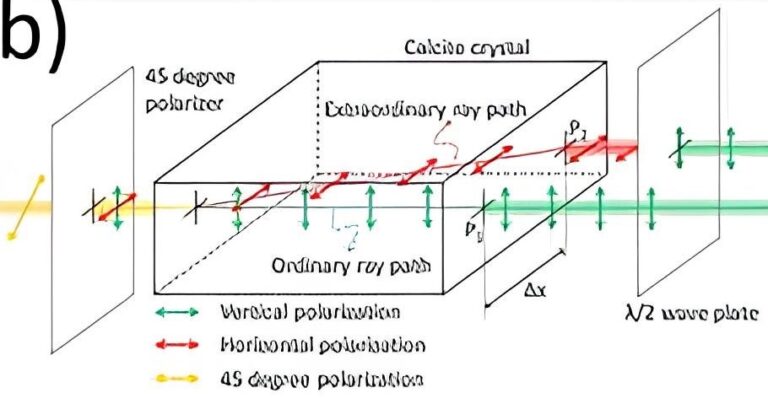
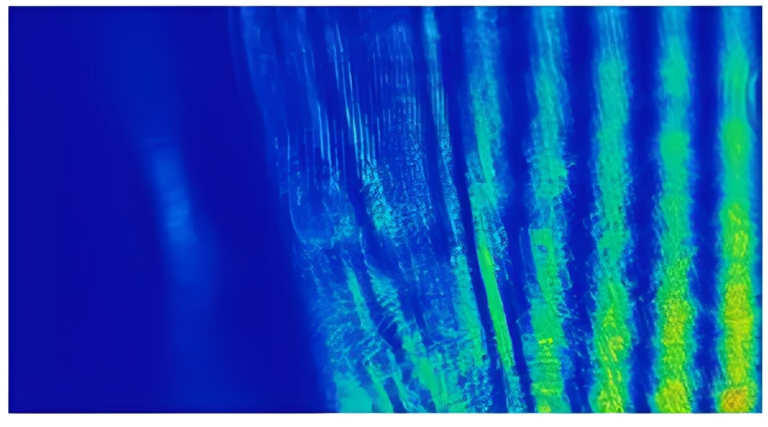
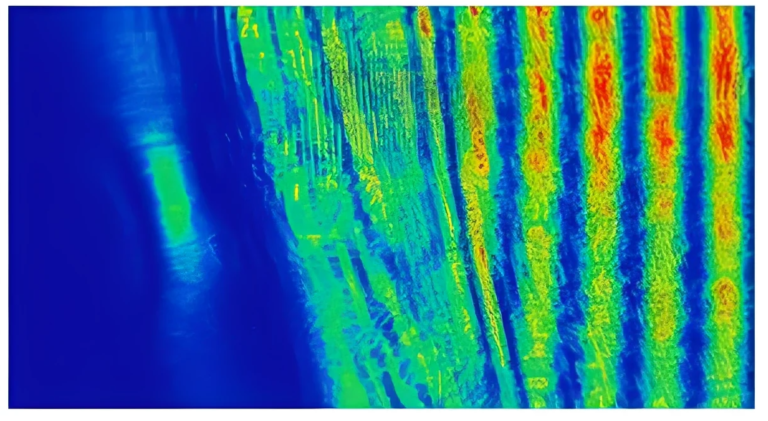
In summary, the ADAMANT project seeks to:
-
Develop a robust quantum communication system implementing high-dimensional quantum protocols for intrinsically secure information transfer.
-
Harness the potential of OAM to facilitate high-density information transfer over long distances, surpassing the limitations of traditional polarization-based systems.
-
Create a communication framework independent of the relative orientation between transmitter and receiver, enhancing practicality in various deployment scenarios.
-
Innovate in the local detection of OAM quantum states through advanced interferometric techniques, broadening the applicability of quantum communication technologies.
Through these objectives, the ADAMANT project endeavors to lay the groundwork for next-generation quantum communication infrastructures, contributing significantly to the realization of a secure and efficient quantum internet.
Referents:
Bruno Paroli, bruno.paroli@unimi.it